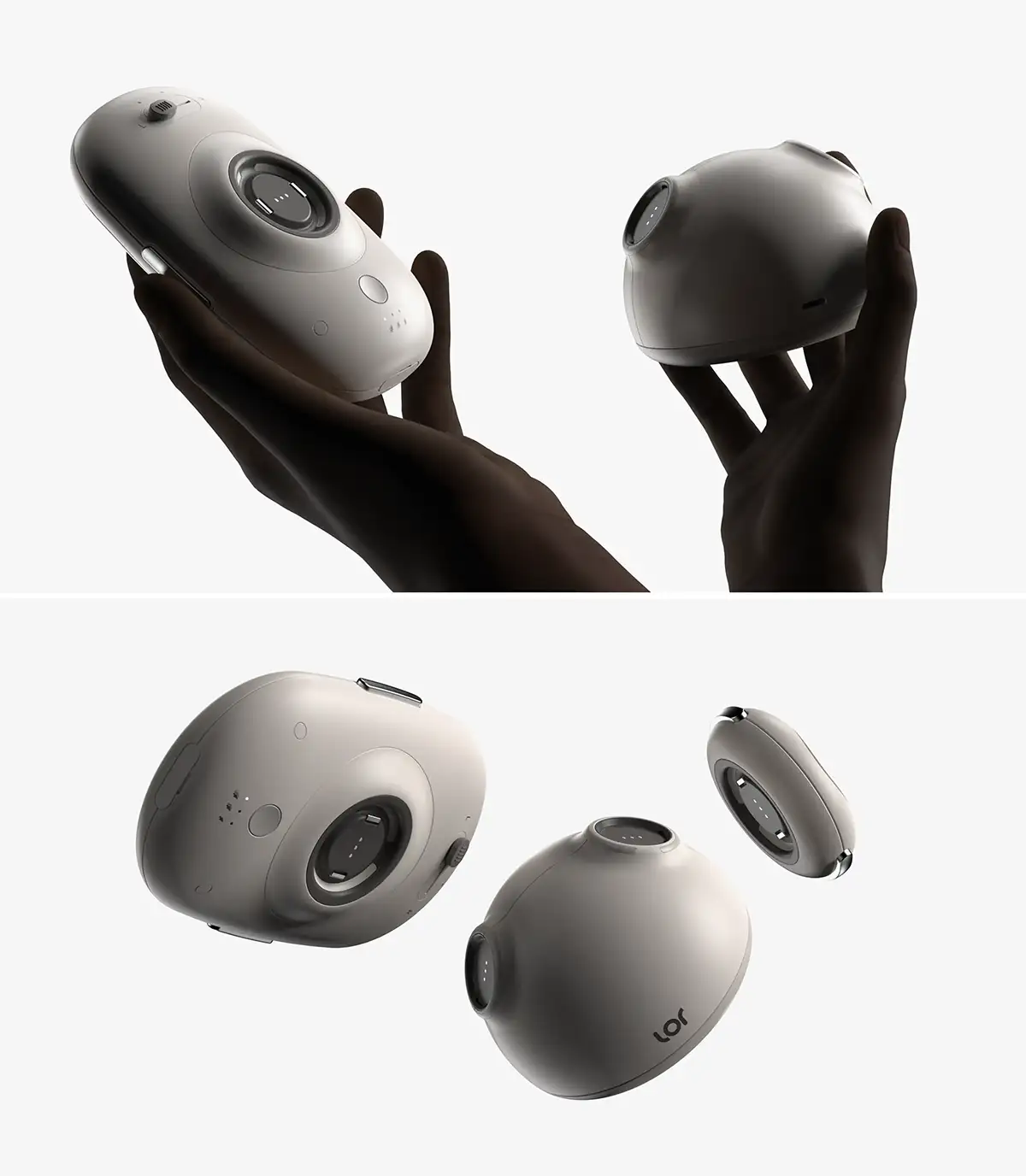
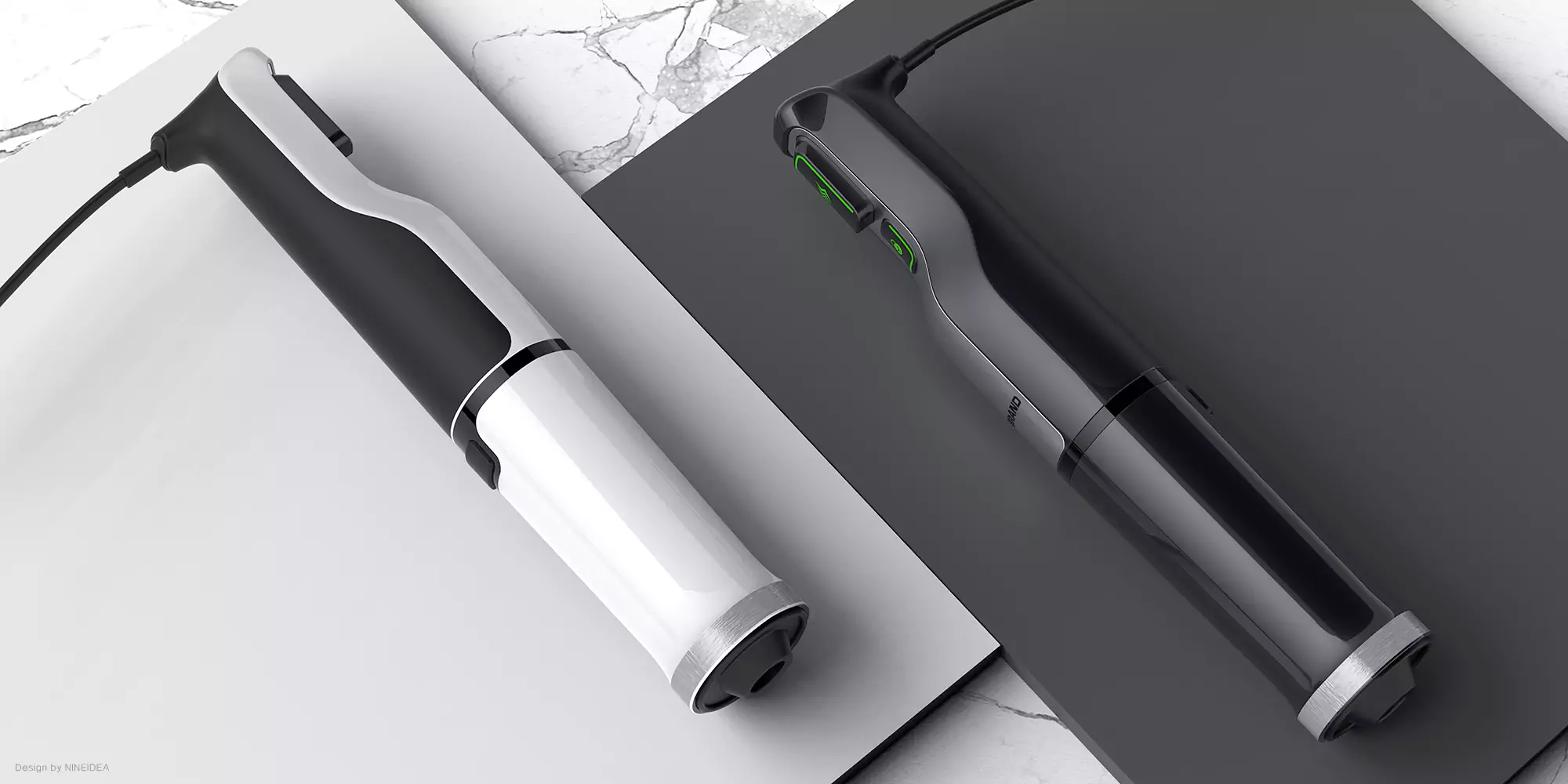
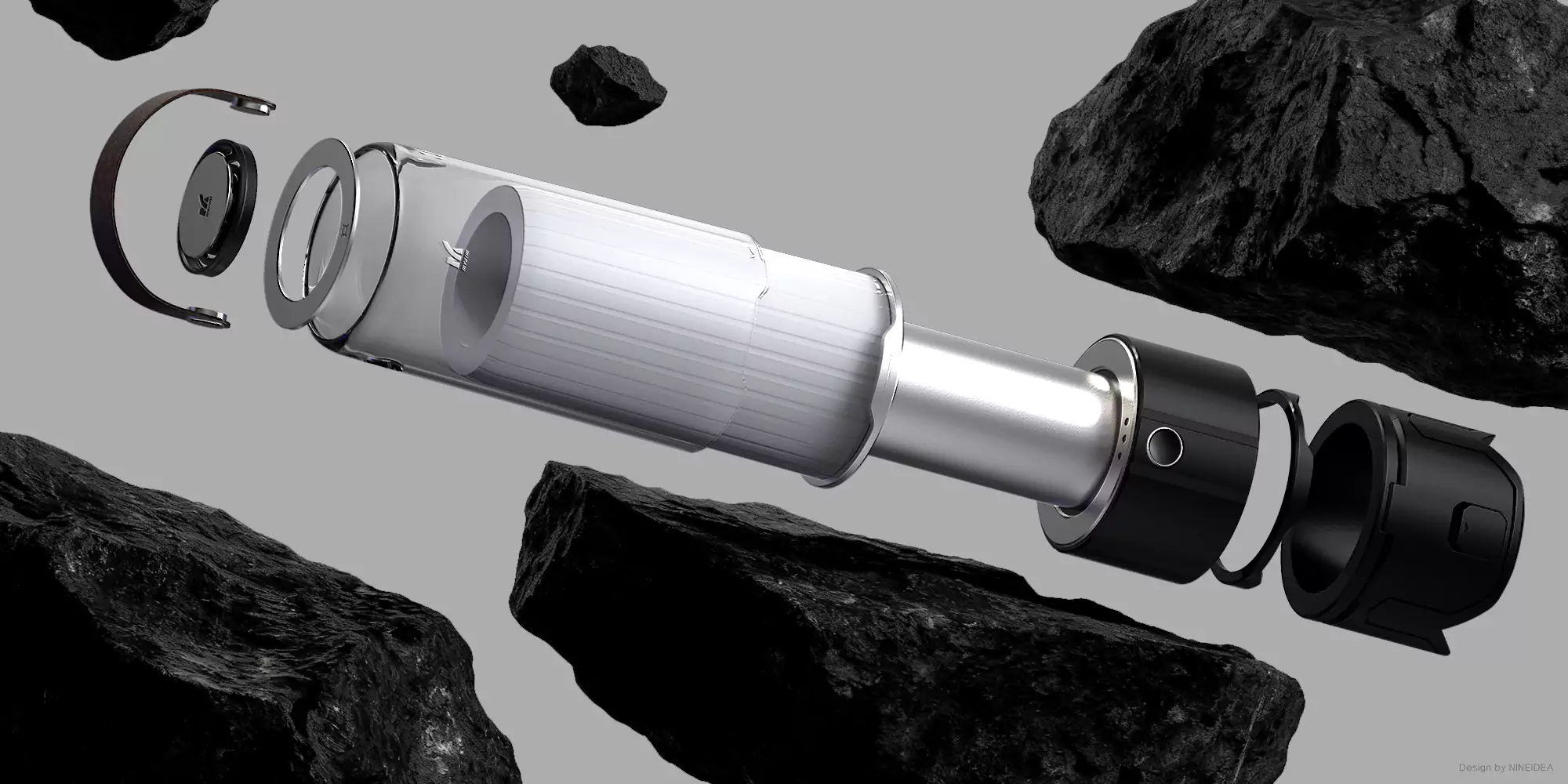
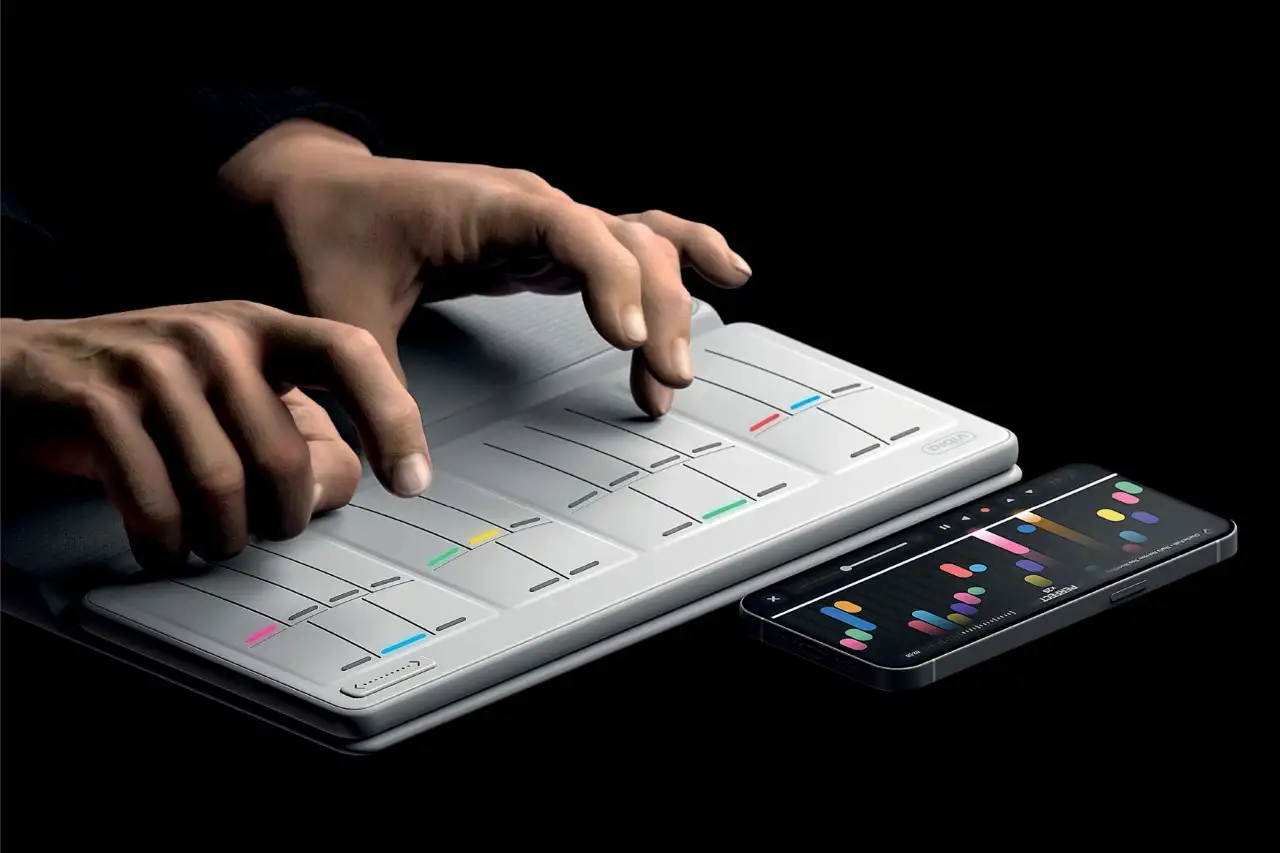
NINEIDEA:工业设计公司设计师的 “黄金年龄” 其实没有一个板上钉钉的答案,它和个人经验积累、技能更新速度、行业需求变化以及职业发展阶段都息息相关。下面咱们从不同角度聊聊,或许能帮你更明白这个职业的特点:
职业成长的阶段特点
- 新手期(0-5 年)
刚入行那几年,设计师大多处于学习阶段,得掌握设计工具,像PS、Rhino、Keyshot 这些软件都得熟,还得了解生产流程、攒项目经验。这时候创意挺活跃,但可能对商业落地、供应链管理这些事儿理解得不够深。
优势:对新技术、潮流反应快,学新工具和设计理念上手快。
挑战:项目经验不够多,得琢磨着怎么平衡创意和实际可行性。 - 成熟期(5-15 年)
工作五六年之后,很多设计师会慢慢进入成熟期,手头有完整的项目经验,能独立带着团队从调研、设计走到量产那一步,同时也明白怎么平衡市场需求、成本控制和用户体验。这时候创意和落地能力磨合得不错,不少人会升到项目经理或者设计主管,得负责团队协作和跨部门沟通。
优势:经验丰富,推动项目落地效率高,既有商业思维又有设计洞察力。
典型年龄段:大概在 30 到 45 岁左右(入行早晚不同,时间会有差别)。 - 资深期(15 年以上)
资深设计师或者行业专家可能会转到战略层面,比如做设计总监、顾问或者自己创业,重点会放在行业趋势判断、前沿技术应用或者跨领域创新(比如产品 + 服务设计或产品+量产服务)上。这时候经验和行业资源成了核心竞争力,职业生命周期能延续到五十岁之后。
优势:在行业里有话语权,擅长整合资源,能带着大家往创新方向走。
核心竞争力的动态变化
- 创意与体力的平衡
二十五六岁到三十五六岁的设计师,可能更有颠覆性的创意,对 Z 世代用户需求、数字化体验(比如 UI/UX 融合)天生敏感,适合快节奏、讲究创新的领域,像消费电子、互联网产品这些。
三十五到五十岁左右的设计师,在复杂项目管理、供应链把控、跨代际用户需求理解上更有优势,适合医疗设备、大型工业产品这些需要深入行业知识的领域。 - 技术迭代与终身学习
工业设计的工具和方法一直在变(比如参数化设计、生成式 AI、虚拟现实建模),能不能持续学习成了延长黄金期的关键。
行业趋势的影响
- 新兴领域的机会
智能硬件、碳中和产品、适老化设计这些新赛道,对设计师的要求更综合了。比如说:- 年轻设计师可能在智能交互、APP 和硬件联动设计上更有优势;
- 资深设计师更擅长把技术趋势和用户深层需求结合起来。
- 跨学科能力的重要性
工业设计不再只盯着外观,而是要和人机工程、材料科学、商业模式设计这些结合起来。不管年龄多大,要是有 “设计 + 技术 + 商业” 的复合能力,职业中期之后可能会迎来新的发展高峰。
打破 “年龄焦虑” 的建议
- 打造自己的独特优势
专注某个细分领域,像医疗设备、交通工具、文创产品,做出别人替代不了的本事。比如,专门做儿童产品设计的设计师,可能 35 岁之后因为特别懂亲子用户的需求,反而更受认可。 - 跟上数字化工具的节奏
学学 AI 辅助设计、云计算协同平台(像 Fusion 360)、元宇宙设计这些,别让工具更新把自己落下。 - 拓宽职业发展的路子
可以往用户体验设计师、设计管理、创新创业这些方向转,或者做自由设计师、行业讲师,让职业生命周期更长。
黄金年龄是经验、创造力、学习力的 “组合拳”
工业设计师的黄金期不是固定在哪岁到哪岁,而是经验积累和持续创新能达到平衡的阶段。一般来讲,多数设计师在 30 到 50 岁之间,综合能力处于高峰,但只要不断突破自己,黄金期能贯穿整个职业生涯。关键不在于年龄多大,而在于是不是一直对行业保持敏感,对技术有好奇心,还能把创意变成实实在在的商业价值。
What is the golden age for designers in industrial design companies?



NINEIDEA: In fact, the “golden age” of designers in industrial design companies does not have a firm answer. It is closely related to the accumulation of personal experience, the speed of skill updating, the change of industry demand and the stage of career development. Let’s talk from different perspectives below, which may help you better understand the characteristics of this profession:
Characteristics of Career Growth Stages
Novice period (0-5 years)
In the first few years of entering the industry, most designers were in the learning stage and had to master design tools such as PS, Rhino, Keyshot, etc. They also had to be familiar with production processes and accumulate project experience. At this point, the creativity is quite active, but the understanding of business implementation and supply chain management may not be deep enough.
Advantages: Quick response to new technologies and trends, quick learning of new tools and design concepts.
Challenge: Lack of project experience, need to figure out how to balance creativity and practical feasibility.
Maturity period (5-15 years)
After working for five or six years, many designers will gradually enter a mature stage, with complete project experience at hand, able to independently lead teams from research, design to mass production, and also understand how to balance market demand, cost control, and user experience. At this point, creativity and practical skills are well integrated, and many people will be promoted to project managers or design supervisors, responsible for team collaboration and cross departmental communication.
Advantages: Rich experience, high efficiency in promoting project implementation, both business thinking and design insight.
Typical age range: around 30 to 45 years old (the timing of entry into the industry may vary).
Senior period (over 15 years)
Senior designers or industry experts may shift to the strategic level, such as becoming a design director, consultant, or starting their own business, with a focus on industry trend judgment, cutting-edge technology applications, or cross disciplinary innovation (such as product+service design or product+mass production services). At this point, experience and industry resources become the core competitiveness, and the career life cycle can continue beyond the age of fifty.
Advantages: Having a say in the industry, adept at integrating resources, and able to lead everyone towards innovation.
Dynamic changes in core competitiveness
Balance between creativity and physical strength
Designers between the ages of 25-36 and 356 may have more subversive ideas. They are naturally sensitive to the needs of Gen Z users and digital experience (such as UI/UX integration), and are suitable for fast-paced and innovative fields, such as consumer electronics and Internet products.
Designers in their thirties to fifties have advantages in complex project management, supply chain control, and understanding of intergenerational user needs, making them suitable for fields such as medical equipment and large industrial products that require in-depth industry knowledge.
Technological iteration and lifelong learning
The tools and methods of industrial design have been constantly changing (such as parametric design, generative AI, virtual reality modeling), and the ability to continuously learn has become the key to extending the golden period.
The impact of industry trends
Opportunities in emerging fields
The requirements for designers in new fields such as smart hardware, carbon neutral products, and aging friendly design have become more comprehensive. for instance:
Young designers may have advantages in intelligent interaction, APP and hardware linkage design;
Senior designers are better at combining technological trends with deep user needs.
The Importance of Interdisciplinary Competence
Industrial design is no longer solely focused on appearance, but should be integrated with ergonomics, materials science, and business model design. No matter how old you are, if you have the composite ability of “design+technology+business”, you may usher in a new peak of development after the middle of your career.
Suggestions for Breaking Age Anxiety
Build your own unique advantages
Focus on a specific niche field, such as medical equipment, transportation, cultural and creative products, and create skills that others cannot replace. For example, designers specializing in children’s product design may be more recognized after the age of 35 due to their special understanding of the needs of parent-child users.
Keep up with the pace of digital tools
Learn AI assisted design, cloud computing collaboration platforms (such as Fusion 360), metaverse design, and don’t let tool updates leave you behind.
Expand career development paths
You can switch to user experience design, design management, innovation and entrepreneurship, or become a freelance designer or industry lecturer to extend your career life cycle.
The golden age is a combination of experience, creativity, and learning ability
The golden age for industrial designers is not fixed at any age, but rather a stage where experience accumulation and continuous innovation can reach a balance. Generally speaking, most designers reach their peak of comprehensive abilities between the ages of 30 and 50, but as long as they constantly break through themselves, the golden period can last throughout their entire career. The key is not about age, but whether one has always been sensitive to the industry, curious about technology, and able to turn ideas into tangible commercial value.