NINEIDEA:当海浪年复一年啃噬着海岸线,全球海滨城镇正面临一场无声的危机 —— 海岸侵蚀不仅让金色沙滩日渐消瘦,更撕裂了滨海生态的平衡。那些曾温柔延伸至水面的沙坡,如今已化作陡峭的崖壁;临时堆砌的沙袋在潮水面前不堪一击,而持续的人工补沙工程,正以高昂的经济成本和生态代价维系着海岸线的脆弱平衡,下面分享一款仿生产品设计,沙滩机器人的生态解决方案。
从海洋生物中汲取的科技灵感
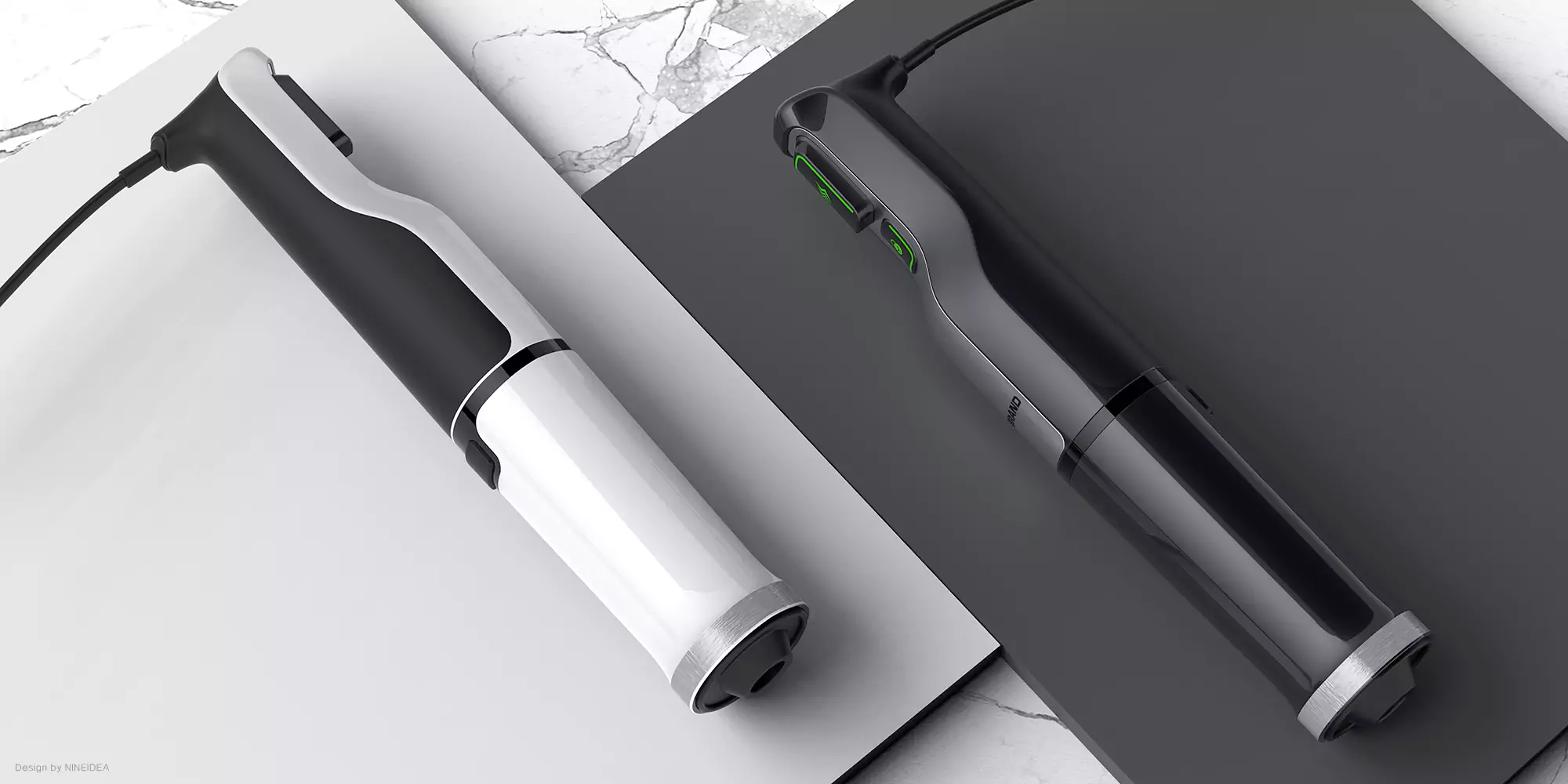
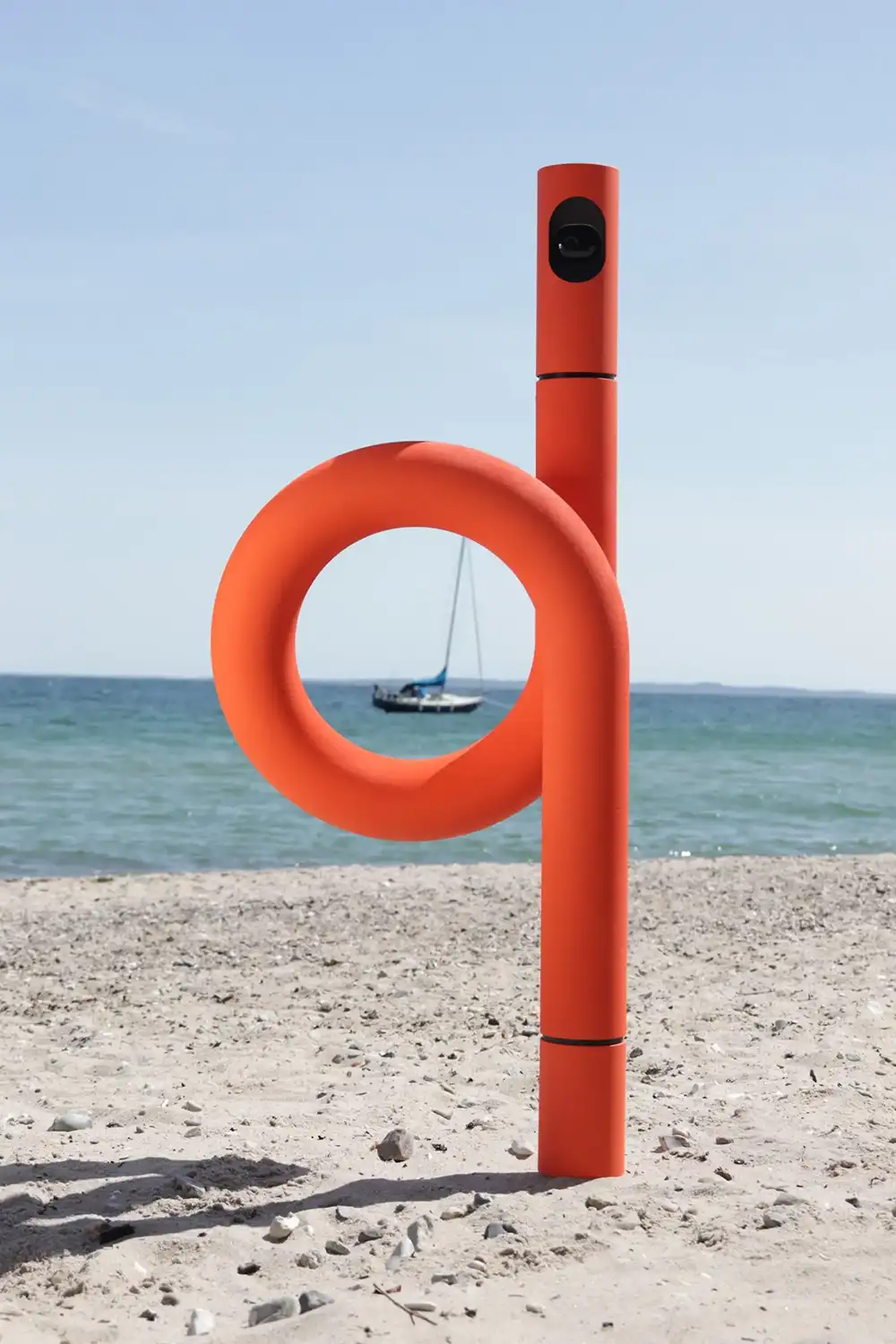
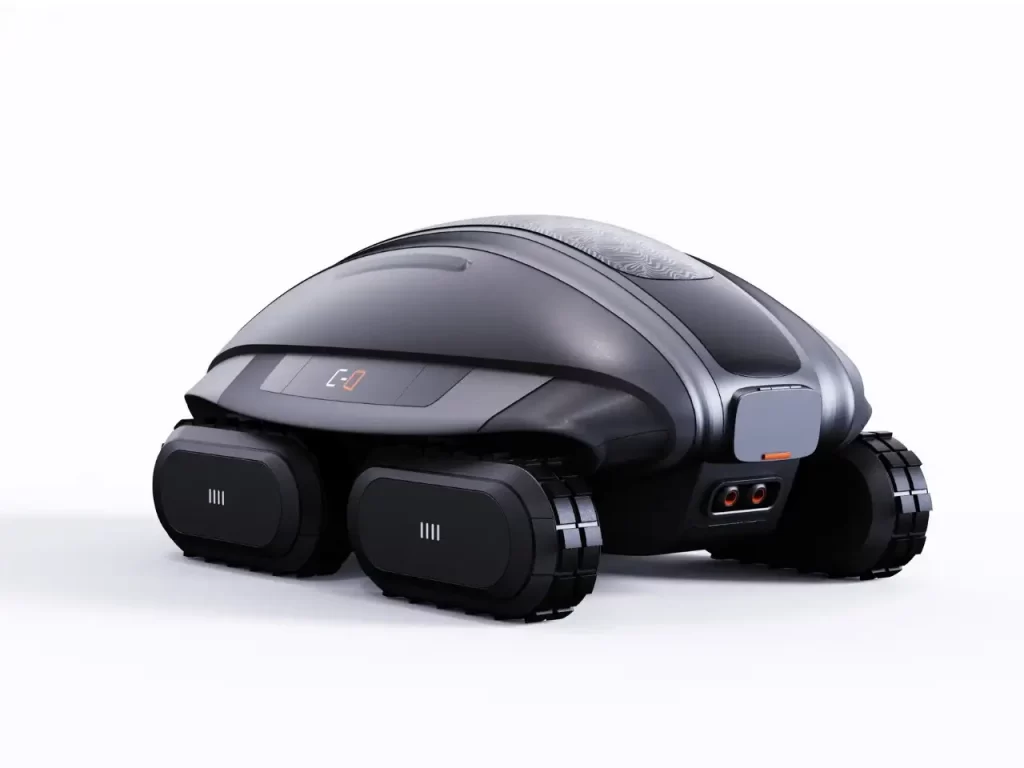
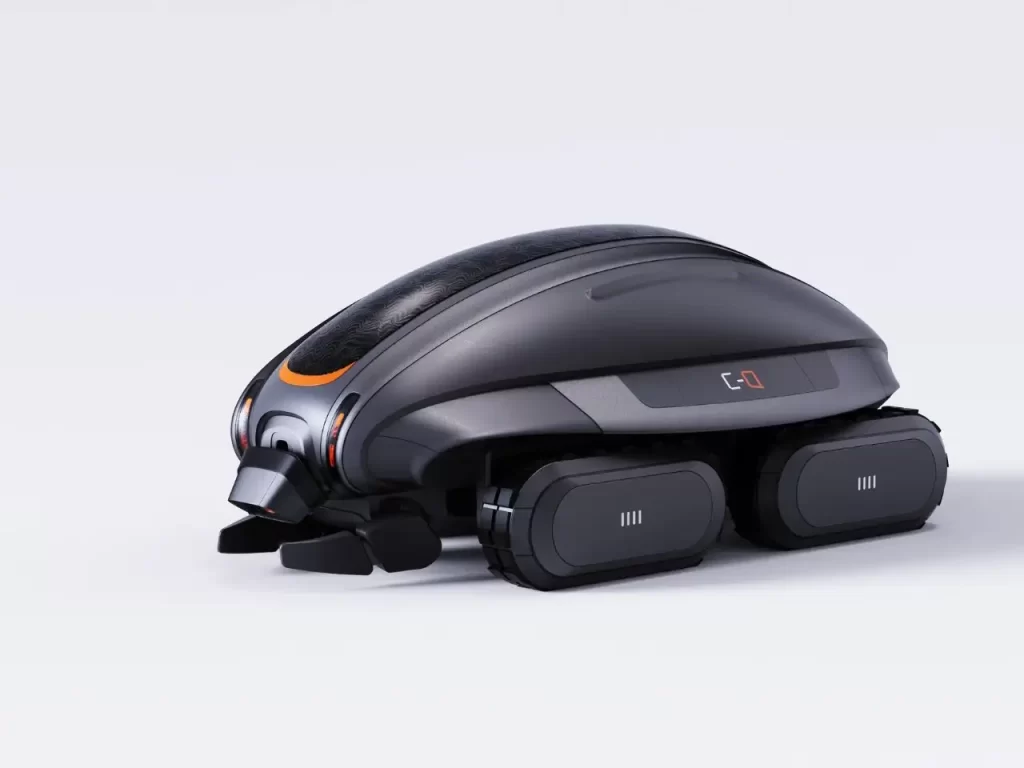
Miyeog K 将目光投向了海洋深处的 “生态工程师”—— 海参。这种其貌不扬的生物通过吞食沙粒、过滤有机物并排出充气化的洁净沙子,默默维系着海底生态的健康循环。受此启发,C-Q 沙机器人以仿生学为核心,构建了一套 “吞噬 – 运输 – 重建” 的动态系统。其圆润流线的机身搭配四驱履带系统,既似科幻电影中的未来机械,又暗含对自然造物的精准复刻。
动态修复:机器人如何重塑海滩?
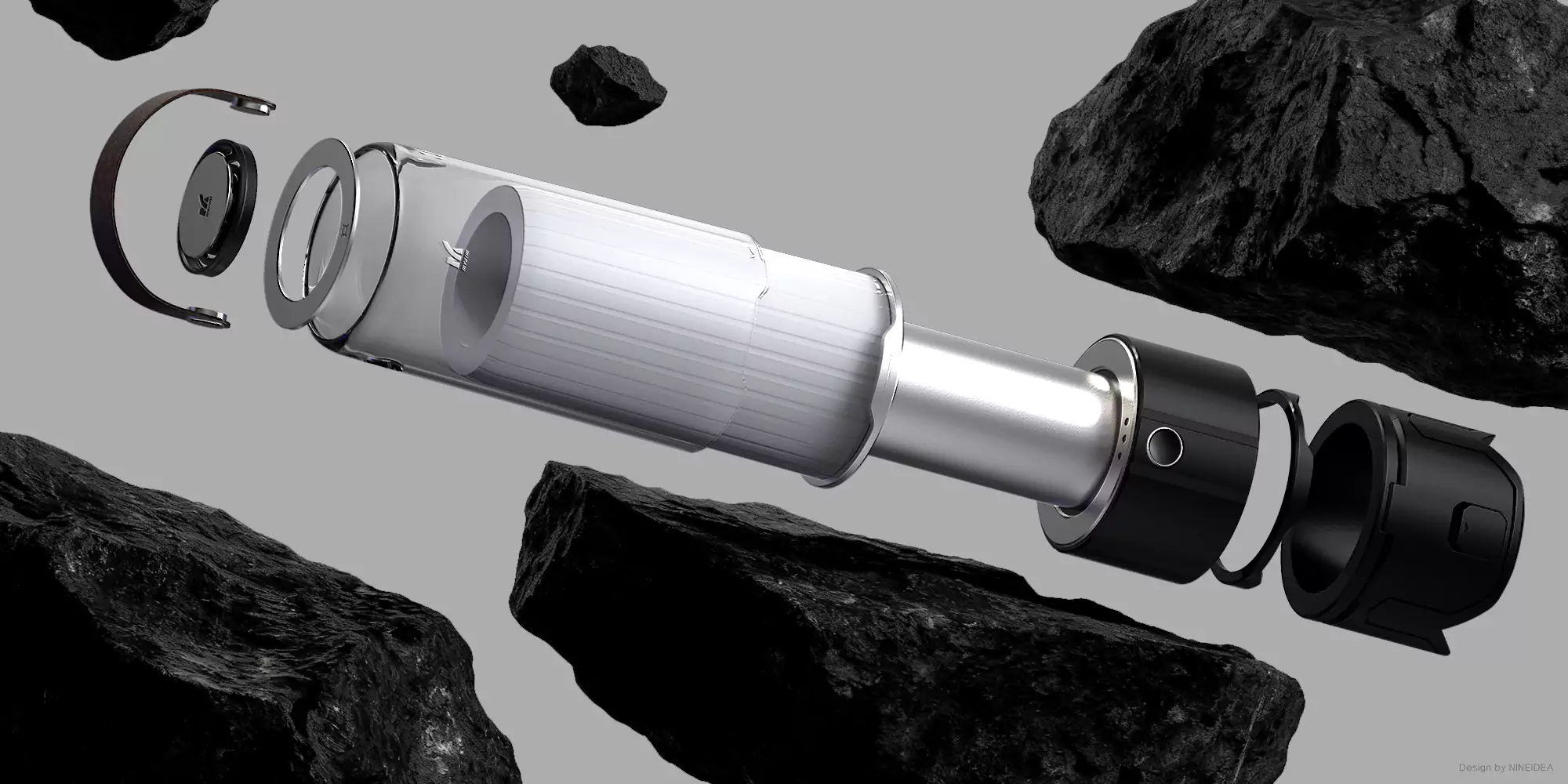
在技术架构上,C-Q 堪称海岸线上的 “移动沙库”:
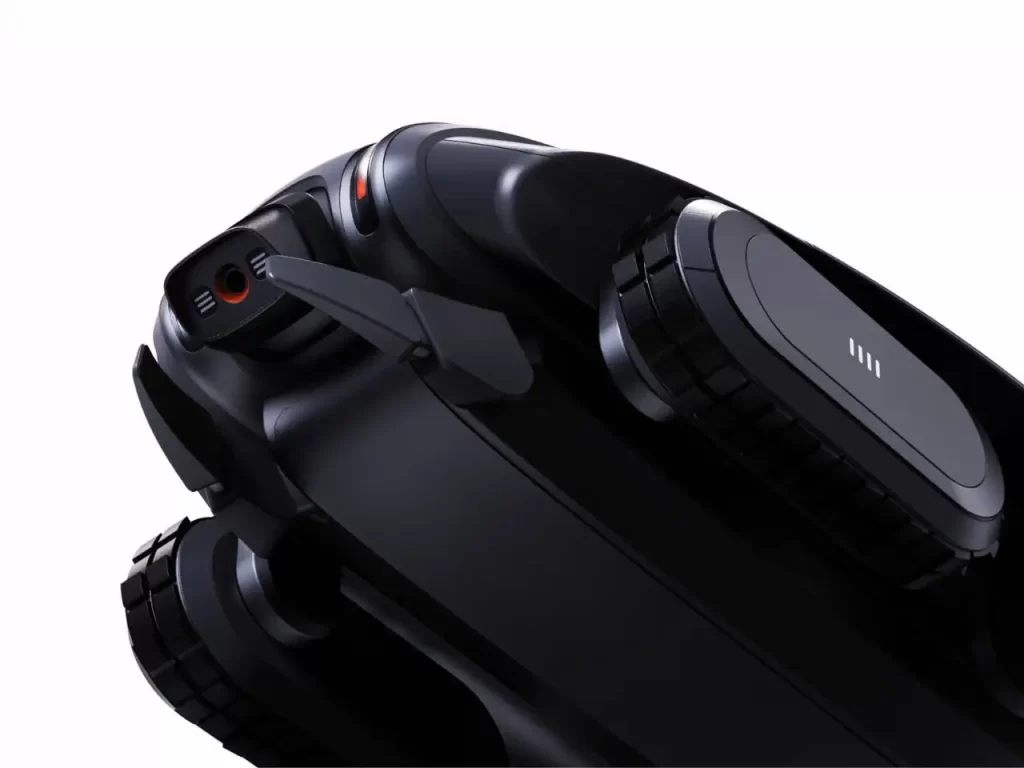
- 全地形作业能力:四条防滑履带赋予其在流沙与浅海区域的灵活机动性,配合防水外壳,可实现 24 小时全天候作业;
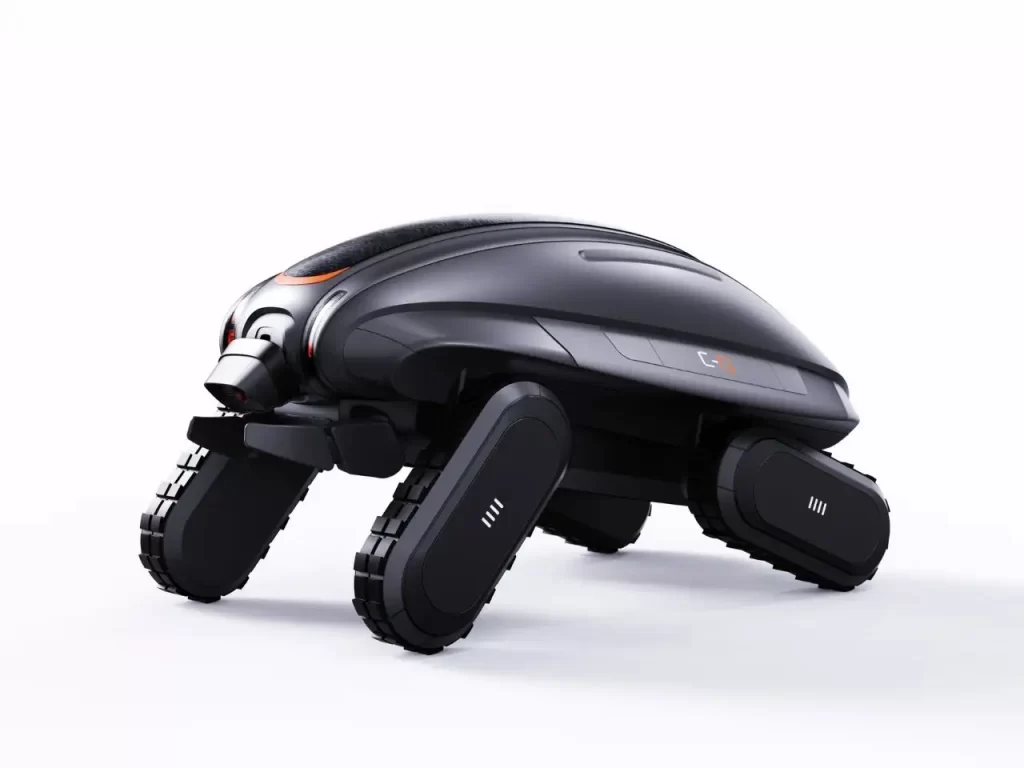
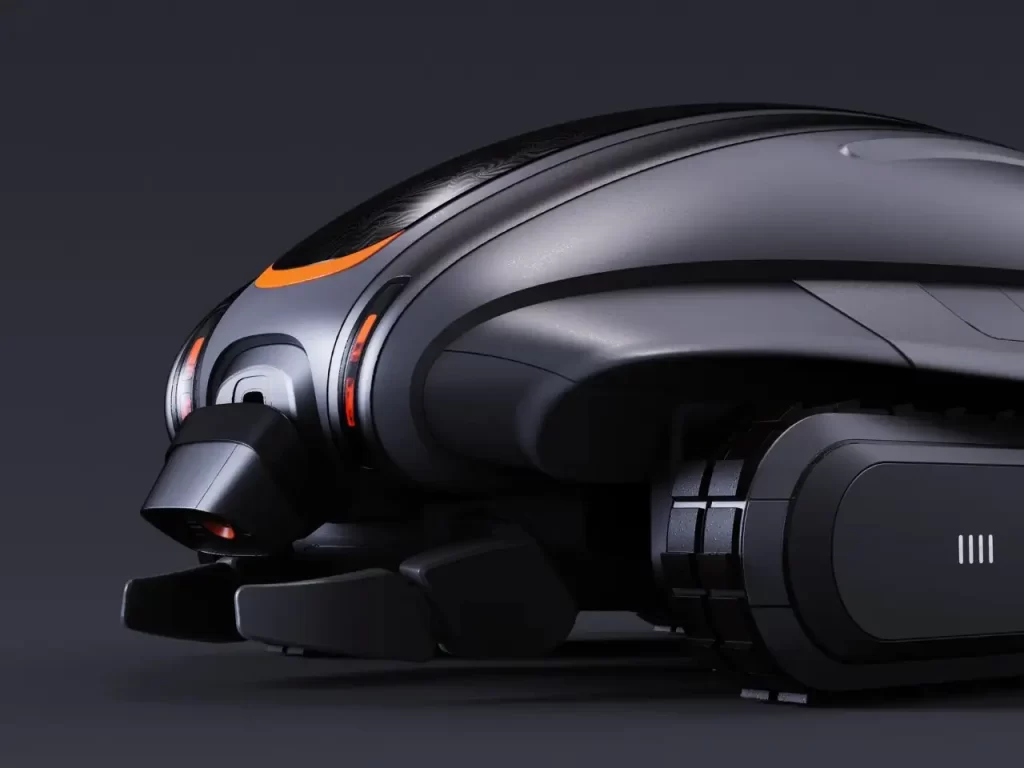
- 智能输沙系统:前端铲斗与负压进气装置能从沙源充足区域高效采集沙粒,体内储沙舱可根据传感器数据精准定位侵蚀地段;
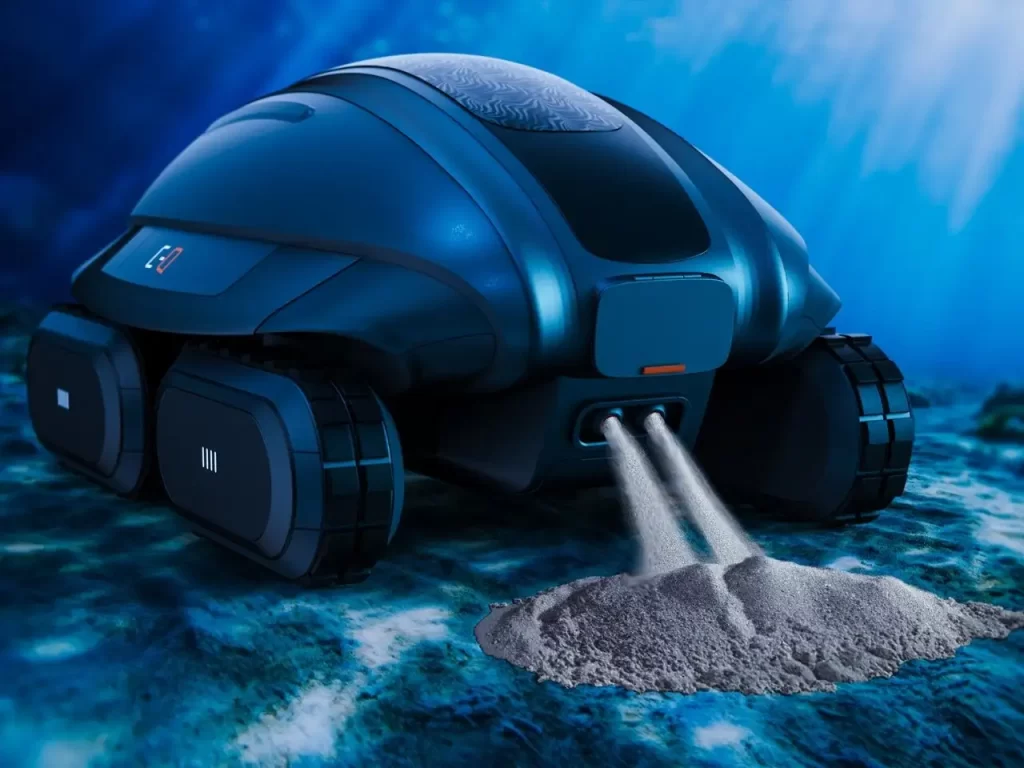
- 生态化释放机制:尾部的分流喷嘴以匀速水流将沙子均匀喷洒至海滩低洼处,模拟自然沉积过程,避免传统机械作业对滩涂生物的惊扰。
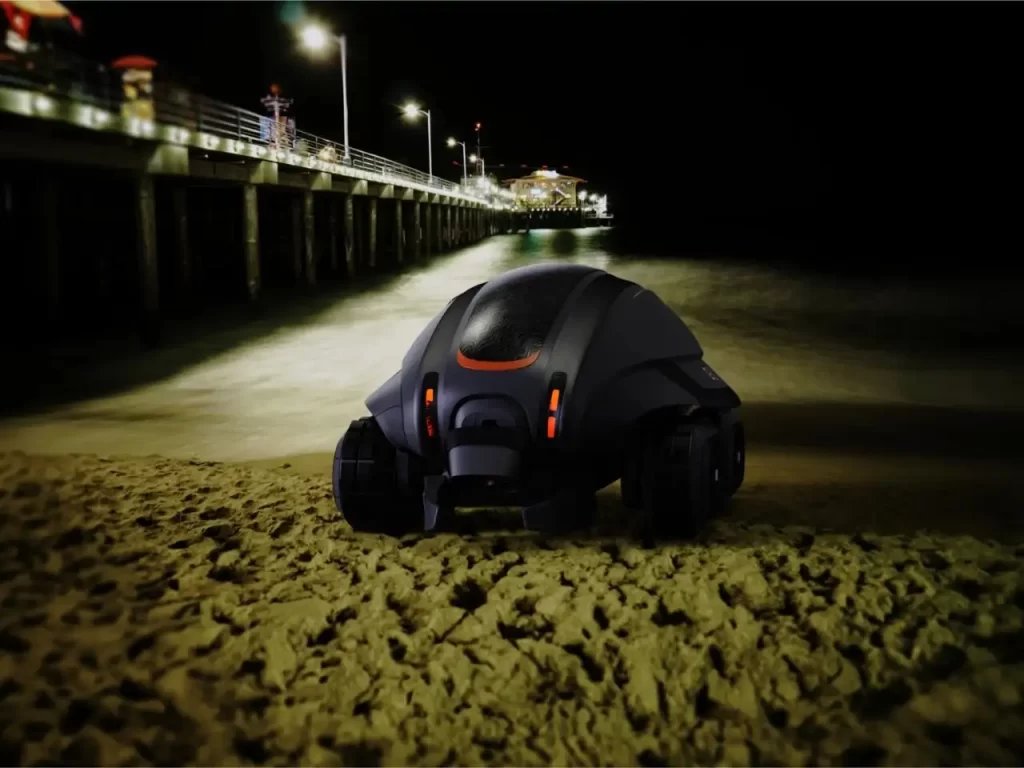
更值得关注的是其绿色能源设计 —— 纯电动驱动系统杜绝了油污污染,而机载 AI 视觉与环境传感器,使其能在夜间自主规避游客与栖息生物,真正实现 “无感修复”。相较于传统重型机械对海岸生态的破坏,C-Q 以毫米级精度的 “温柔操作”,让补沙工程从 “应急抢救” 升级为 “生态重塑”。
从概念到未来:科技与自然的共生可能
尽管 C-Q 目前仍处于概念阶段,但其展现的创新逻辑已为海岸防护提供了全新思路:当仿生科技与生态需求深度融合,人类不再需要以对抗的姿态 “抵御” 自然,而是通过智能工具参与自然循环。想象一群 C-Q 机器人在暮色中沿着海岸线静默作业,它们吞吐沙粒的节奏与潮汐韵律共振,终将让萎缩的海滩重获新生 —— 那时,我们或许能真正躺在沙滩上,安心享受日光浴,让科技成为守护自然的伙伴,而非凌驾其上的主宰。
这场关于海岸线的 “机器人革命”,本质上是一次对 “向自然学习” 的实践印证:当海参用亿万年的进化书写生态智慧,C-Q 则以科技语言将其转译为守护地球的力量 —— 这或许正是解决环境难题的终极答案:不是征服,而是共生。








C-Q SAND ROBOT CONCEPT CAN HELP STOP COASTAL EROSION
NINEIDEA: As the waves gnaw at the coastline year after year, the global coastal towns are facing a silent crisis – coastal erosion not only makes the golden beach thinner, but also tears the balance of coastal ecology. The sand slopes that once gently extended to the surface of the water have now turned into steep cliffs; Temporary sandbags are vulnerable to the tide, while continuous artificial sand replenishment projects are maintaining the fragile balance of the coastline at high economic and ecological costs. Below is a biomimetic product design, an ecological solution for beach robots.
Technological inspiration drawn from marine organisms
Miyeog K turned his attention to the “ecological engineer” of the deep ocean – sea cucumber. This unremarkable creature silently maintains the healthy cycle of underwater ecology by devouring sand particles, filtering organic matter, and expelling aerated clean sand. Inspired by this, the C-Q sand robot has built a dynamic system of “phagocytosis transport reconstruction” with biomimetics as its core. Its rounded and streamlined body, coupled with a four-wheel drive track system, resembles both futuristic machinery from science fiction movies and a precise replica of natural creations.
Dynamic Restoration: How Robots Reshape the Beach?
In terms of technical architecture, C-Q can be regarded as a “mobile sandbox” on the coastline:
All terrain operation capability: Four anti slip tracks endow it with flexible maneuverability in quicksand and shallow sea areas, and with a waterproof shell, it can achieve 24-hour all-weather operation;
Intelligent sand transport system: The front-end bucket and negative pressure intake device can efficiently collect sand particles from areas with sufficient sand sources, and the internal sand storage compartment can accurately locate erosion areas based on sensor data;
Ecological release mechanism: the distributary nozzle at the tail evenly sprays sand to the low-lying area of the beach with uniform flow, simulating the natural sedimentation process, and avoiding the disturbance of traditional mechanical operations on mudflat organisms.
What is more noteworthy is its green energy design – the pure electric drive system eliminates oil pollution, while the onboard AI vision and environmental sensors enable it to autonomously avoid tourists and living organisms at night, truly achieving “sensory restoration”. Compared to the damage caused by traditional heavy machinery to coastal ecology, C-Q has upgraded sand replenishment projects from “emergency rescue” to “ecological reshaping” with millimeter level precision in “gentle operation”.
From Concept to Future: The Potential for Symbiosis between Technology and Nature
Although C-Q is still in the conceptual stage, its innovative logic has provided new ideas for coastal protection: when bionic technology is deeply integrated with ecological needs, humans no longer need to “resist” nature in a confrontational manner, but participate in the natural cycle through intelligent tools. Imagine a group of C-Q robots silently operating along the coastline in the twilight, their rhythm of sucking and swallowing sand resonating with the rhythm of tides, ultimately giving a new life to the shrinking beach – at that time, we may be able to truly lie on the beach, enjoy sunbathing with peace of mind, and let technology become a partner in protecting nature, rather than a master above it.
This “robot revolution” about coastlines is essentially a practical verification of “learning from nature”: when sea cucumbers use billions of years of evolution to write ecological wisdom, C-Q translates it into a technological language to protect the earth – this may be the ultimate answer to solving environmental problems: not conquest, but symbiosis.